Scientific Editor: Editorial Board ISUD website
What is Microsurgical Varicocele Repair?
Varicocele is an abnormal enlargement of the pampiniform venous plexus (testicular veins) in the scrotum. Microsurgical Varicocele Repair is the surgical procedure to ligate the dilated testicular veins, in order to prevent venous blood from flowing backwards and avoid all consequent harmful effects related to testicular function.
When is it performed?
Varicoceles usually develop during adolescence but not all varicocele cases need to be treated. Indications for treatment are:
- Abnormal semen parameters in the spermiogram
- Progressive testicular atrophy, starting during puberty
- Testicular pain, not attributed to any other cause
What preparation is required?
There has to be a recent spermiogram as a point of reference. In some cases, your physician may ask for sperm storage and cryopreservation (sperm freezing) before the surgical procedure. Upon hospital admission, preoperative preparation includes blood tests, chest X-ray and ECG (electrocardiogram). In case you are on anticoagulant therapy, it may be required to interrupt your anticoagulant therapy a few days before the operation. You should always consult your Cardiologist, for there may be need to replace anticoagulants with injections in the abdominal region.
How is it performed?
The procedure is usually performed under general anesthesia, with patient sleeping throughout surgery. It can be either laparoscopic or open surgery.
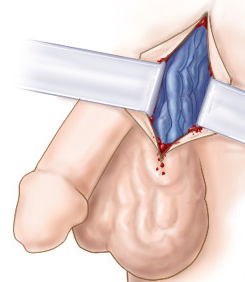
In open surgery, a small incision is made either low in the groin or higher in the abdomen where spermatic veins are identified and ligated. This inguinal approach with the use of a microscope is known as ‘microsurgery’. Microsurgery allows the surgeon to have direct visual access, minimizes complication rate and promotes the patient’s faster recovery.
In the laparoscopic method, a mini camera is inserted through small skin incisions that are made in the abdomen. This camera transfers a high-resolution image on the screen so that the surgeon can visualize the target region and operate with the use of instruments that are attached to the camera.
The average hospital stay is 2 days. However, if feeling good, the patient can leave hospital on the very same day.
What about after the procedure?
Upon discharge from hospital, you will receive specific instructions about:
- when it is safe to restart your previous anticoagulant therapy
- when it is safe to resume to intense physical exercise and work
- what antibiotic regimen to take
- when to have your next semen analysis
If there are absorbable stitches, these have to be removed within 7 to 10 days from surgery.
What is the effect on patient’s quality of life?
Most patients do not face any problem after surgery. It usually takes 14 days for the wound to fully heal. It takes the patient 2-4 weeks to fully recover and resume to normal life. It is possible to resume to a typical office work even 1-2 days after surgery.
After surgery, a small percentage of patients may present:
- Varicocele recurrence, over time. With the microsurgery method, though, recurrence rate drops to less than 3%.
- Hydrocele (presence of fluid in the scrotal sac). This is the most common complication with non-microsurgical techniques. However, this risk is almost eliminated with the method of microsurgical varicocele repair.


