- What is Epididymitis?
- What are the causes and risk factors of eEpididymitis?
- What are the symptoms of Epididymitis?
- How is Epididymitis diagnosed?
- How is Epididymitis treated?
- Can there be complications from Epididymis?
What is Epididymitis?
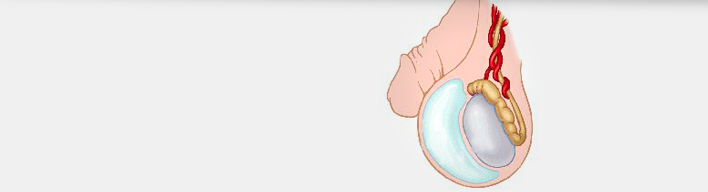
Epididymis is the inflammation of epididymis, which is the organ connecting the testis with the seminal duct. The spermatozoa that are produced in the testis pass through the epididymis to end up in the seminal duct. If there is simultaneous inflammation in the testis as well, then the disease is called Testicular Epididymitis. It may occur at all ages but it is more common in men aged 19-35 years old.
What are the causes and risk factors of Epididymitis?
Epididymitis usually occurs due to the spread of some bacterial urethral or bladder infection. There is difference between the bacteria causing epididymitis in young and in aged men. In rare cases, epididymitis may be caused by MTB (Mucobacterium tuberculosis).
Among risk factors, the most common ones are:
- Recent urinary tract surgery (e.g. transurethral prostatectomy, circumcision and varicocelectomy)
- Permanent use of urocatheter
- After intense sexual activity without protection or with multiple sex partners
What are the symptoms of Epididymitis?
Epididymitis may initially appear with fever, sensation of heaviness in the scrotal area and tenderness on palpation. Afterwards, the testis swells and becomes particularly hard and painful.
Other symptoms are:
- Weakness, fatigue
- Hemospermia
- Lower abdominal discomfort
- Pain in the groin
- Painful ejaculation
- Urinary frequency/ Dysurea
How is Epididymis diagnosed?
In the beginning, the physician takes the patient's detailed medical history and performs a thorough clinical examination. If considered essential, the patient may be asked to undergo some specific tests, such as:
- General blood testing
- General urine test and culture (to check whether there is concomitant urinary tract infection)
- Testicular ultra sound (U/S) screening
It is important for the physician to be able to differentiate between epididymitis and testicular torsion. Testicular Torsion is an emergency condition which needs to be immediately surgically treated.
How is Epididymitis treated?
As long as your general health condition is good, the physician will prescribe oral pharmacotherapy (antibiotics, anti-inflammatories, antipyretics). At the same time you will be asked to rest for some days and keep scrotal area elevated, with the use of a jockstrap (an undergarment supporter designed for supporting male genitalia). In some cases, there may be need for hospitalization and intravenous pharmaceutical treatment. Epididymitis is usually fully resolved within 3-4 weeks taking proper drug regimen, without having any effect on the patient's reproductive capacity.
Can there be complications from Epididymitis?
Although rarely occuring, there may be some complications, such as:
- Hydrocele (fluid collection around one testis). Althouth this is a common condition, the fluid is usually absorbed on its own.
- Scrotal abscess, probably requiring surgical treatment
- Chronic epididymitis
- Testicular damage
- Infertility